Mobile Phone Technology
5G Mobile Network Architecture
image ©tucanaThere are 2 variants of 5G in the Uk; 5G-SA (Stand Alone) and 5G-NR (New Radio). 5G-NR has the 5G radio / wireless infrastructure but it is connected to the 4G core to send the data to the Internet. 5G-SA is the full end to end 5G which includes a new core to the network.
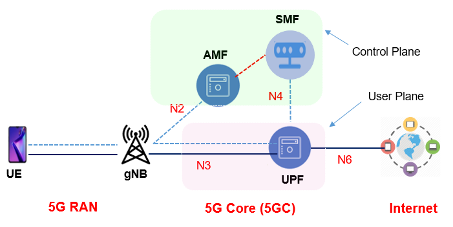
The User Equipment (UE) will connect wirelessly to a mast. This includes all the technology to manage the equipment connected to the mast itself, and to pass on the data to the core network. The device is the next generation NodeB (gNb).
The core of the 5G network (realised in 5G-SA) is split into 2 planes, the user plane (UP) and the control plane (CP)
The user plane is the part of the core that connects the UE to the Internet. This is managed by a UPF (User Plane Function) that is distributed between an edge location and a centre location. This is in an attempt to speed up the network, and lower the latency. Whenever possible the edge will manage the UPF functions thus distributing the tasks putting them nearer the user where possible, connecting to an edge data centre.
There are two aspects to the Control Plane; firstly the AMF (Access and Mobility Management Function). The AMF manages the access to the network, authenticating the UE and access to the 5G network. To allow the AMF to do it's task it needs access to the necessary data. In 5G-SA this is contained in a UDR (Unified Data Repository). This will be a distributed data store, accessed via various APIs to facilitate the distribution and access. The data can be moved to the edge to again speed up the functions of the AMF.
The SMF manages the data sessions for the UE whilst on the 5G network. Interfaces with the User Plane that manages the data transfer.
© mobilephonetechnology.co.uk all rights reserved 2017-2025
